As the fourth industrial revolution unfolds, the modern factory floor is transforming into a fluid, intelligent environment where machines, materials, and data move with precision and autonomy. At the heart of this transformation is factory automation, and one critical backbone of this evolution is automated material handling.
Today, how materials are transported within a plant, from raw material storage to machine loading, in-process transfer, to final dispatch, is no longer a secondary consideration. With shrinking batch sizes, rising labour costs, demand for traceability, and the need for continuous production, smart material handling systems are becoming a decisive lever for productivity, quality, and agility.
What are the key technologies driving this change? Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), Gantry Systems, Conveyors, and Industrial Robots are reshaping the shopfloor.
The global drive towards automation
According to Interact Analysis, the global market for material handling equipment is expected to grow from $35 billion in 2023 to over $50 billion by 2028, with AMRs and robotic solutions leading the charge. The IFR (International Federation of Robotics) reports that over 121,000 mobile robots were deployed globally in 2022, representing a 44% year-on-year increase. This trend aligns with the growing demand for flexible, lights-out manufacturing.
1. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): Flexible in-plant logistics
Unlike traditional AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) that rely on fixed paths or magnetic strips, AMRs use lidar, cameras, and AI to dynamically navigate factory layouts, reroute around obstacles, and make intelligent decisions in real-time.
Why AMRs?
- They adapt to layout changes, which is critical in high-mix, low-volume (HMLV) manufacturing setups.
- Reduce non-value-adding human motion to enhance worker safety and uptime.
Applications
- Moving pallets or bins between the warehouse and the machines
- Delivering tools or components to assembly lines
- Intra-cell transportation in modular production lines

2. Gantry Systems: High-Speed, High-Precision Transfer
Gantry robots are ideal for rapid, repeatable material movement along linear axes. Typically mounted overhead or integrated into machine tool lines, gantries can handle heavy loads and execute precise pick-and-place operations at high speeds.
Key Benefits
- Consistent cycle times
- Space-saving by utilising overhead space
- Integrated easily with CNC and PLC systems
Applications
- Machine tending in CNC lines
- Palletising and de-palletising
- Handling components between machining and inspection
🎯 Trend: Hybrid systems are emerging, where gantries work in tandem with AMRs – gantries for precision loading, AMRs for cross-floor transport.
3. Conveyor Systems: The proven workhorse gets smarter
Conveyors are the most established form of automated transport. What’s changing today is how smart sensors, motorised rollers, and IoT connectivity are turning them into intelligent, responsive systems.
Modern Upgrades
- Modular conveyors allow reconfiguration for product changes
- IoT-enabled systems for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance
- Zero-pressure accumulation improves energy efficiency and safety
Applications
- Moving parts between machining stations
- Final product transfer to packing areas
- Accumulation and buffering in assembly lines
🔍 Insight: The use of vision systems and weight sensors with conveyors allows inline quality checks and sorting, integrating quality assurance directly into the flow.
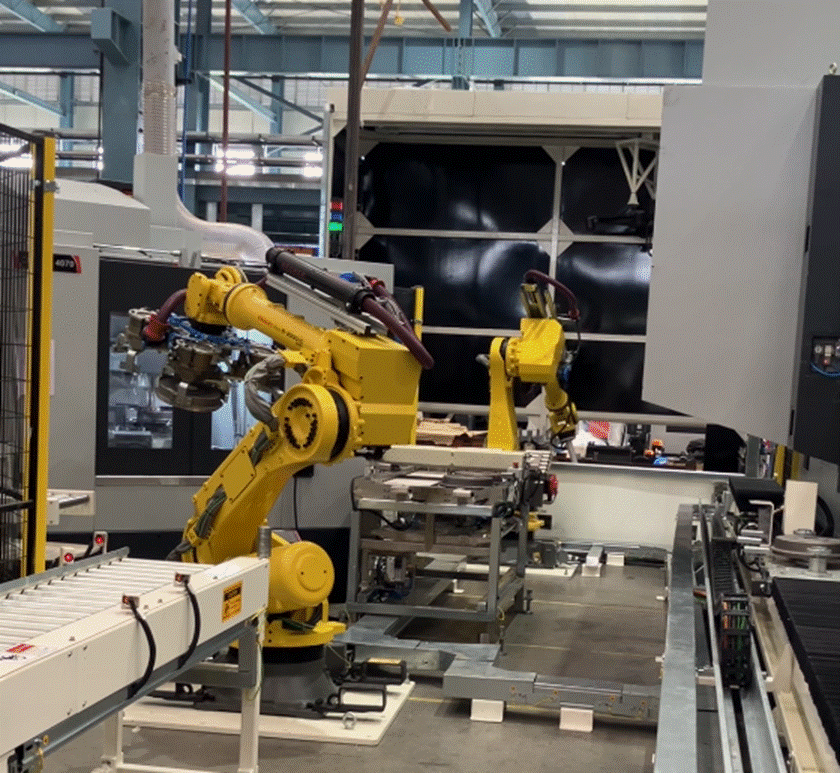
4. Robotic Arms for Material Handling: Beyond pick-and-place
Industrial robots are no longer confined to repetitive pick-and-place. With 6-axis and collaborative robots (cobots), factories are achieving precision handling of delicate or high-variability components.
Trends to watch
- AI-powered path planning: Enabling robots to handle disordered parts
- Cobots + AMRs: A mobile manipulator can deliver and pick components on the move
- End-of-arm tooling (EOAT) innovations: Quick-change grippers and multi-purpose tools
Applications:
- Bin picking with 3D vision
- Loading/unloading from CNC or injection molding machines
- Handling in hazardous or cleanroom environments
The integration challenge and opportunity
While each of these systems offers standalone benefits, the real competitive edge lies in integration. The convergence of MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), WMS (Warehouse Management Systems), PLCs, and cloud-based monitoring enables a seamless flow from incoming materials to finished products.
According to a Deloitte study, manufacturers who implemented end-to-end automated material handling systems reported a 20% increase in throughput, a 40% reduction in lead time, and a 30% improvement in inventory accuracy.
From motion to intelligence
In the new age of manufacturing, motion isn’t just about moving parts – it’s about moving intelligently. Smart material handling systems are the silent enablers of leaner, faster, and more responsive production.
As AMRs become smarter, gantries more compact, conveyors more adaptive, and robots more collaborative, the factory floor is evolving from a sequence of operations into an orchestrated performance of automation and autonomy.
For manufacturers ready to embrace Industry 4.0, investing in integrated material handling is not just about cost saving; it’s about future-proofing operations for agility, traceability, and resilience.