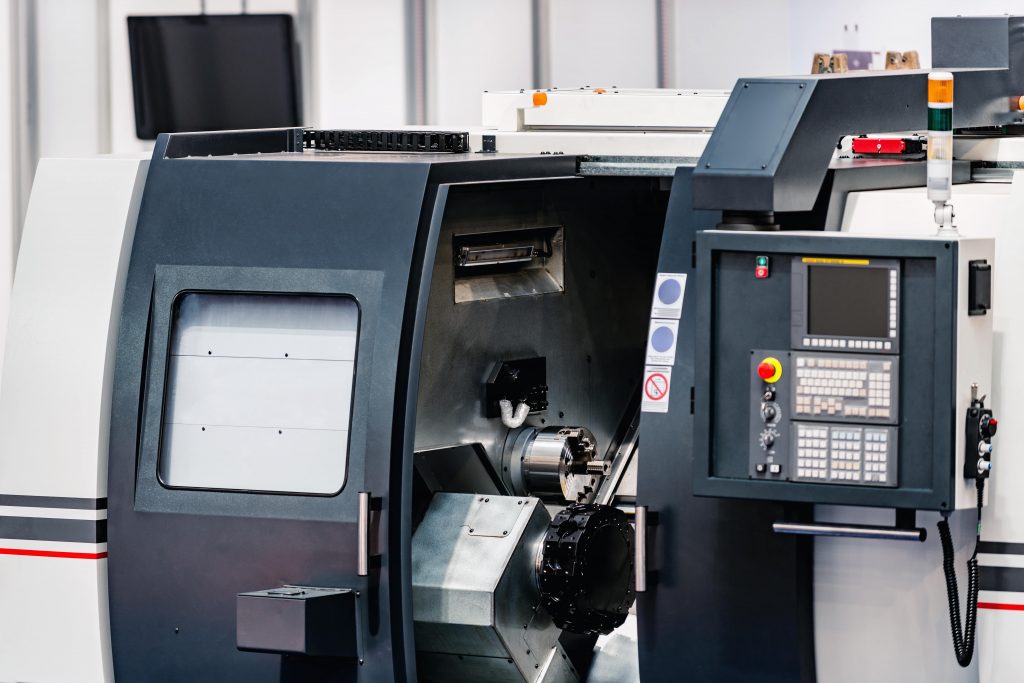
In modern manufacturing, the demand for accuracy, speed, and complexity has never been higher. From aerospace to medical technology, industries require components with intricate geometries and flawless precision. This is where 5-axis CNC machines stand out—delivering unmatched flexibility and efficiency compared to traditional 3-axis setups.
Understanding what 5-axis CNC machining is, how it works, and why it matters gives engineers and manufacturers a clear view of how advanced machining drives the future of production.
What is a 5-axis CNC machine
A 5-axis CNC machine is a computer-controlled machining center that moves a cutting tool or a workpiece along five different axes simultaneously. In addition to the standard three linear axes (X, Y, and Z), two additional rotary axes (commonly A and B, or B and C) are introduced. This enables the tool to approach the workpiece from virtually any angle, enhancing the capabilities of the machining process.
Unlike 3-axis machines, where the part must be repositioned multiple times to access different faces, 5-axis machining allows complex parts to be completed in a single setup. This not only improves accuracy but also reduces cycle time and eliminates the risk of misalignment from re-clamping.
How 5-axis CNC machining works
The key to 5-axis machining lies in simultaneous multi-axis movement. While the cutting tool rotates at high speed, the machine’s computer numerical control (CNC) system synchronizes the movement of all axes. This allows the tool to maintain optimal cutting orientation relative to the workpiece surface.
- Linear axes (X, Y, Z) – Standard movements that position the tool along the three-dimensional plane.
- Rotary axes (A, B, or C) – These axes tilt or rotate the workpiece or the tool head, enabling cutting from multiple angles.
- CNC control system – Executes G-code instructions to coordinate toolpaths with extreme accuracy.
- Toolpath programming – Generated using CAD/CAM software, toolpaths are optimized to reduce tool wear, minimize cycle times, and maintain surface quality.
This level of control makes 5-axis CNC machining particularly well-suited for parts with curved surfaces, deep cavities, or complex contours.
Key parts of a 5-axis CNC machine
While similar in structure to other CNC machining centers, 5-axis machines incorporate additional hardware for greater flexibility:
- Spindle – Rotates the cutting tool at variable speeds, designed for high precision and rigidity.
- Rotary table or trunnion – Provides the additional axes of rotation, either by rotating the workpiece (table configuration) or tilting the spindle head (head configuration).
- Machine table – Holds the workpiece in place, often integrated with a rotary unit for 5-axis operation.
- Control panel – Interface for loading programs, adjusting cutting parameters, and monitoring performance.
- Automatic tool changer (ATC) – Enables multiple operations in one cycle without manual intervention.
- Coolant and chip management systems – Essential for high-speed cutting and maintaining surface finish on complex parts.
Types of 5-axis CNC machines
Not all 5-axis CNC machines are built the same. The two most common configurations are:
- Head/Head configuration – Both rotary axes are located in the spindle head. This allows the tool to tilt and rotate, offering excellent flexibility for complex geometries.
- Table/Head configuration – One rotary axis is built into the spindle head, and the other into the machine table. This setup balances flexibility and rigidity, making it versatile for various part sizes.
- Table/Table configuration – Both rotary axes are integrated into the table. This is ideal for smaller workpieces and provides excellent stability.
Benefits of 5-axis CNC machining
- Single-setup machining – With 5-axis technology, even highly complex parts can be machined in one setup instead of requiring multiple fixtures and re-clamping. This not only saves time but also eliminates errors caused by repositioning the workpiece, which is a common source of dimensional inaccuracy in 3-axis machining.
- Higher precision – By reducing or eliminating the need to transfer parts between machines or setups, 5-axis machining ensures that all features are produced in perfect relation to one another. The CNC system synchronizes movements across all axes, allowing tight tolerances to be achieved consistently.
- Ability to machine complex geometries – The extra rotary axes allow cutting tools to reach angles and surfaces that would otherwise be impossible. This makes 5-axis machining ideal for components with freeform surfaces, deep cavities, undercuts, and intricate contours, often found in aerospace, medical, and mold-making applications.
- Improved surface finish – Since the tool can remain closer to a normal cutting angle across curved surfaces, tool deflection and vibration are minimized. This leads to smoother tool engagement, reduced step-over marks, and superior surface quality—often eliminating the need for secondary finishing processes.
- Shorter lead times – 5-axis machines reduce cycle time by consolidating operations, minimizing setup changes, and optimizing toolpaths. Faster production of complex parts means manufacturers can respond more quickly to customer demands, supporting agile and just-in-time manufacturing.
- Material efficiency – The ability to orient the cutting tool at optimal angles reduces excess material removal, improves chip evacuation, and extends tool life. This not only lowers tooling costs but also enhances sustainability by minimizing scrap and rework.
Applications of 5-axis CNC machines
5-axis CNC machining is widely used in industries where precision and complexity are critical:
- Aerospace – Turbine blades, impellers, and structural components.
- Medical – Orthopedic implants, surgical instruments, and dental components.
- Automotive and motorsport – Engine parts, molds, and high-performance components.
- Energy – Complex components for turbines, oil and gas equipment, and renewable systems.
- Tool and die making – Molds, dies, and intricate prototypes.
Conclusion
5-axis CNC machines represent the pinnacle of modern machining technology. By combining precision, flexibility, and efficiency, they enable manufacturers to produce highly complex parts in less time and with greater accuracy. For industries facing increasing demands for innovation and quality, 5-axis machining is not just an option—it’s a necessity.